背景
前面我们描述了spring profile和maven profile的异同maven profile VS spring profile
通常意义上我们说的配置一般都是properties文件,但是spring支持yml【结构程度更好】
EnableConfigurationProperties
原先我们在使用Spring时更多的是使用value注解进行注入,但是对于比较多的属性的情况下
也只能一味的进行复制拷贝
Spring支持了EnableConfigurationProperties
/** * Enable support for {@link ConfigurationProperties} annotated beans. * {@link ConfigurationProperties} beans can be registered in the standard way (for * example using {@link Bean @Bean} methods) or, for convenience, can be specified * directly on this annotation. * * @author Dave Syer */ @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableConfigurationProperties { /** * Convenient way to quickly register {@link ConfigurationProperties} annotated beans * with Spring. Standard Spring Beans will also be scanned regardless of this value. * @return {@link ConfigurationProperties} annotated beans to register */ Class<?>[] value() default {}; }
对于EnableConfigurationProperties import EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector
该selector做了如下操作
class EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector implements ImportSelector { @Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) { MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes = metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes( EnableConfigurationProperties.class.getName(), false); Object[] type = attributes == null ? null : (Object[]) attributes.getFirst("value"); if (type == null || type.length == 0) { return new String[] { ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessorRegistrar.class .getName() }; } return new String[] { ConfigurationPropertiesBeanRegistrar.class.getName(), ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessorRegistrar.class.getName() }; } /** * {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar} for configuration properties support. */ public static class ConfigurationPropertiesBeanRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes = metadata .getAllAnnotationAttributes( EnableConfigurationProperties.class.getName(), false); List<Class<?>> types = collectClasses(attributes.get("value")); for (Class<?> type : types) { String prefix = extractPrefix(type); String name = (StringUtils.hasText(prefix) ? prefix + "-" + type.getName() : type.getName()); if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(name)) { registerBeanDefinition(registry, type, name); } } } private String extractPrefix(Class<?> type) { ConfigurationProperties annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(type, ConfigurationProperties.class); if (annotation != null) { return annotation.prefix(); } return ""; } private List<Class<?>> collectClasses(List<Object> list) { ArrayList<Class<?>> result = new ArrayList<Class<?>>(); for (Object object : list) { for (Object value : (Object[]) object) { if (value instanceof Class && value != void.class) { result.add((Class<?>) value); } } } return result; } private void registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Class<?> type, String name) { BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder .genericBeanDefinition(type); AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = builder.getBeanDefinition(); registry.registerBeanDefinition(name, beanDefinition); ConfigurationProperties properties = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(type, ConfigurationProperties.class); Assert.notNull(properties, "No " + ConfigurationProperties.class.getSimpleName() + " annotation found on '" + type.getName() + "'."); } } } 而事实上的处理位置在 @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") private void postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName, ConfigurationProperties annotation) { Object target = bean; PropertiesConfigurationFactory<Object> factory = new PropertiesConfigurationFactory<Object>( target); factory.setPropertySources(this.propertySources); factory.setValidator(determineValidator(bean)); // If no explicit conversion service is provided we add one so that (at least) // comma-separated arrays of convertibles can be bound automatically factory.setConversionService(this.conversionService == null ? getDefaultConversionService() : this.conversionService); if (annotation != null) { factory.setIgnoreInvalidFields(annotation.ignoreInvalidFields()); factory.setIgnoreUnknownFields(annotation.ignoreUnknownFields()); factory.setExceptionIfInvalid(annotation.exceptionIfInvalid()); factory.setIgnoreNestedProperties(annotation.ignoreNestedProperties()); if (StringUtils.hasLength(annotation.prefix())) { factory.setTargetName(annotation.prefix()); } } try { factory.bindPropertiesToTarget(); } catch (Exception ex) { String targetClass = ClassUtils.getShortName(target.getClass()); throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Could not bind properties to " + targetClass + " (" + getAnnotationDetails(annotation) + ")", ex); } }
可以看到prefix会被设置到targetname中 而targetname将会被包装秤Releaxedname
private Iterable<String> getRelaxedTargetNames() { return (this.target != null && StringUtils.hasLength(this.targetName) ? new RelaxedNames(this.targetName) : null); }
而relaxedname如下
/** * Create a new {@link RelaxedNames} instance. * @param name the source name. For the maximum number of variations specify the name * using dashed notation (e.g. {@literal my-property-name} */ public RelaxedNames(String name) { this.name = (name == null ? "" : name); initialize(RelaxedNames.this.name, this.values); } @Override public Iterator<String> iterator() { return this.values.iterator(); } private void initialize(String name, Set<String> values) { if (values.contains(name)) { return; } for (Variation variation : Variation.values()) { for (Manipulation manipulation : Manipulation.values()) { String result = name; result = manipulation.apply(result); result = variation.apply(result); values.add(result); initialize(result, values); } } }
将会包装成多个【大小写 驼峰等等】望文生义
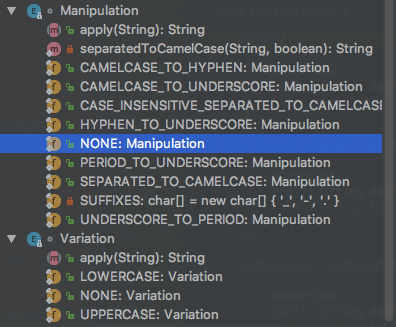
总之通过各种异形的名称来在属性文件中获取到设置的值
下面和以前Spring3一样通过setPropertyValue来设置对应的值。
PropertySource
其中有一个random特别引起了开发者的欢迎。
比如可以如下定义
my: secret: password: ${random.value} intValue: ${random.int} intValueRange: ${random.int[1,99]} longValue: ${random.long} longValueRange: ${random.long[111111111111,999999999999]} uuid: ${random.uuid}
来查看
/** * {@link PropertySource} that returns a random value for any property that starts with * {@literal "random."}. Where the "unqualified property name" is the portion of the * requested property name beyond the "random." prefix, this {@link PropertySource} * returns: * <ul> * <li>When {@literal "int"}, a random {@link Integer} value, restricted by an optionally * specified range.</li> * <li>When {@literal "long"}, a random {@link Long} value, restricted by an optionally * specified range.</li> * <li>Otherwise, a {@code byte[]}.</li> * </ul> * The {@literal "random.int"} and {@literal "random.long"} properties supports a range * suffix whose syntax is: * <p> * {@code OPEN value (,max) CLOSE} where the {@code OPEN,CLOSE} are any character and * {@code value,max} are integers. If {@code max} is provided then {@code value} is the * minimum value and {@code max} is the maximum (exclusive). * * @author Dave Syer * @author Matt Benson */ public class RandomValuePropertySource extends PropertySource<Random> { /** * Name of the random {@link PropertySource}. */ public static final String RANDOM_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "random"; private static final String PREFIX = "random."; private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(RandomValuePropertySource.class); public RandomValuePropertySource(String name) { super(name, new Random()); } public RandomValuePropertySource() { this(RANDOM_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME); } @Override public Object getProperty(String name) { if (!name.startsWith(PREFIX)) { return null; } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Generating random property for '" + name + "'"); } return getRandomValue(name.substring(PREFIX.length())); } private Object getRandomValue(String type) { if (type.equals("int")) { return getSource().nextInt(); } if (type.equals("long")) { return getSource().nextLong(); } String range = getRange(type, "int"); if (range != null) { return getNextIntInRange(range); } range = getRange(type, "long"); if (range != null) { return getNextLongInRange(range); } if (type.equals("uuid")) { return UUID.randomUUID().toString(); } return getRandomBytes(); } private String getRange(String type, String prefix) { if (type.startsWith(prefix)) { int startIndex = prefix.length() + 1; if (type.length() > startIndex) { return type.substring(startIndex, type.length() - 1); } } return null; } private int getNextIntInRange(String range) { String[] tokens = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(range); int start = Integer.parseInt(tokens[0]); if (tokens.length == 1) { return getSource().nextInt(start); } return start + getSource().nextInt(Integer.parseInt(tokens[1]) - start); } private long getNextLongInRange(String range) { String[] tokens = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(range); if (tokens.length == 1) { return Math.abs(getSource().nextLong() % Long.parseLong(tokens[0])); } long lowerBound = Long.parseLong(tokens[0]); long upperBound = Long.parseLong(tokens[1]) - lowerBound; return lowerBound + Math.abs(getSource().nextLong() % upperBound); } private Object getRandomBytes() { byte[] bytes = new byte[32]; getSource().nextBytes(bytes); return DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(bytes); } public static void addToEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { environment.getPropertySources().addAfter( StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, new RandomValuePropertySource(RANDOM_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)); logger.trace("RandomValuePropertySource add to Environment"); } }
非常有意思
properties 加载顺序
至于实现profile的关键
spring 解析对应properties通过 PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) { if (this.propertySources != null) { for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" + propertySource.getName() + "'"); } Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key); if (value != null) { if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) { value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value); } logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value); return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType); } } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source"); } return null; }
可以看出propertySources的顺序非常影响对应注入的参数【当查找到第一个符合条件的结果后就返回了】
那么我们最经常用的在Jvm参数中 -Dspring.active.profile=dev
关于JVM参数中-D
-D<name>=<value> set a system property 设置系统属性。
这样相当于在environment中设置了spring.active.profile
因此部分小伙伴碰到在properties定义属性为
user.name发现无法生效【这是因为在系统中已经存在比properties优先级更高的系统环境变量】
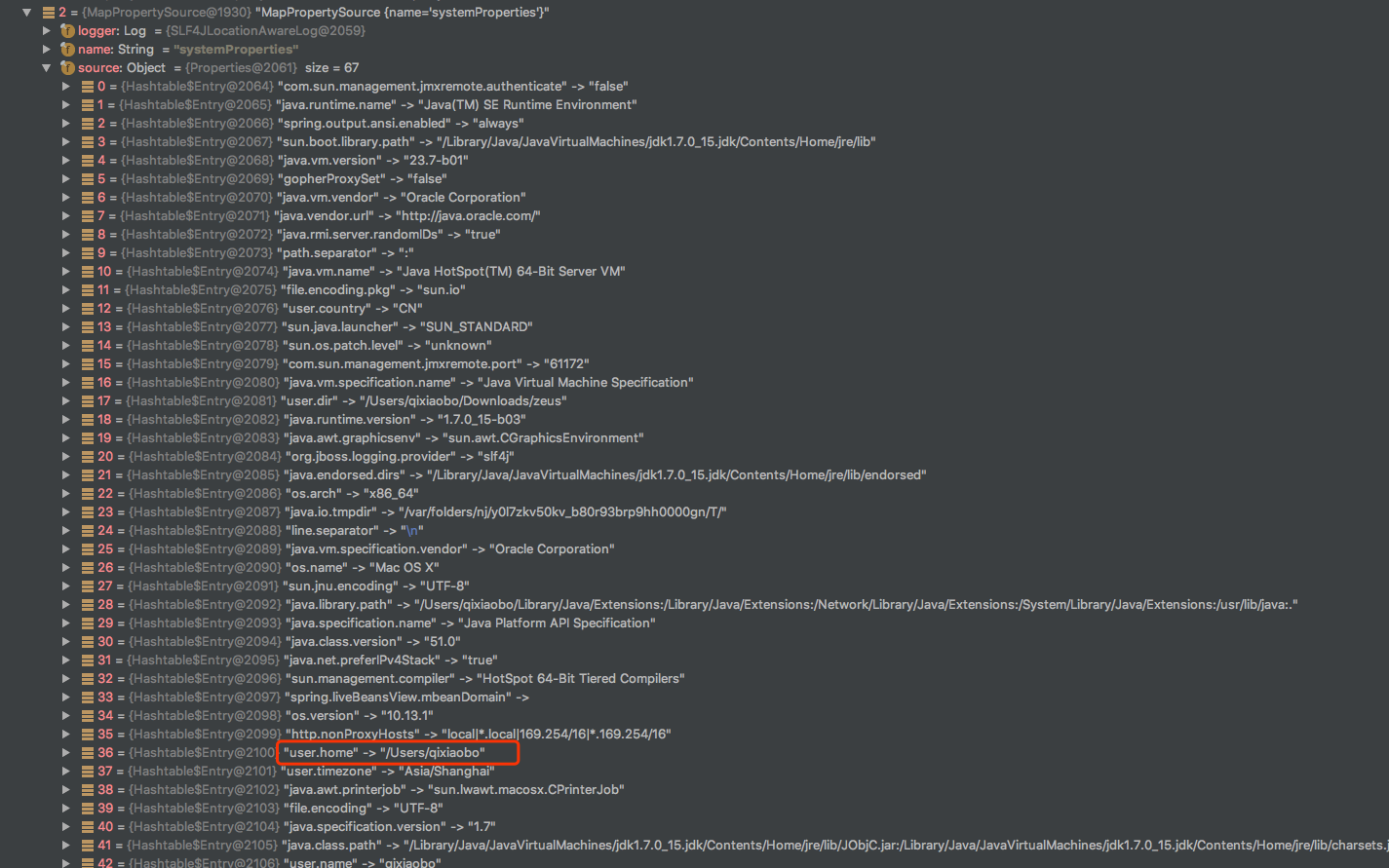
如何确认propertySource的优先级顺序呢?
SpringBoot在启动时或默认配置如下
/** * Add, remove or re-order any {@link PropertySource}s in this application's * environment. * @param environment this application's environment * @param args arguments passed to the {@code run} method * @see #configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment, String[]) */ protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) { MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources(); if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) { sources.addLast( new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties)); } if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) { String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME; if (sources.contains(name)) { PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name); CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name); composite.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource( name + "-" + args.hashCode(), args)); composite.addPropertySource(source); sources.replace(name, composite); } else { sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args)); } } }
可以看到我们可以设置默认defaultProperties 如果存在将会设置到最后
但是对于java调用参数【如果存在】来说默认会将其放入第一位
对于标准环境来说Spring默认也会调用如下方法
/** * Create a new {@code Environment} instance, calling back to * {@link #customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources)} during construction to * allow subclasses to contribute or manipulate {@link PropertySource} instances as * appropriate. * @see #customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources) */ public AbstractEnvironment() { customizePropertySources(this.propertySources); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Initialized " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " with PropertySources " + this.propertySources); } } /** * Customize the set of property sources with those appropriate for any standard * Java environment: * <ul> * <li>{@value #SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME} * <li>{@value #SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME} * </ul> * <p>Properties present in {@value #SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME} will * take precedence over those in {@value #SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME}. * @see AbstractEnvironment#customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources) * @see #getSystemProperties() * @see #getSystemEnvironment() */ @Override protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) { propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties())); propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment())); }
因此将会放入对应的propertySource【在做Environment的构造函数时】因此在创建完成时
SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
分别出现在properties前两位【直到放入commandArgument】
对于servlet容器
/** * Customize the set of property sources with those contributed by superclasses as * well as those appropriate for standard servlet-based environments: * <ul> * <li>{@value #SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME} * <li>{@value #SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME} * <li>{@value #JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME} * </ul> * <p>Properties present in {@value #SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME} will * take precedence over those in {@value #SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME}, and * properties found in either of the above take precedence over those found in * {@value #JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME}. * <p>Properties in any of the above will take precedence over system properties and * environment variables contributed by the {@link StandardEnvironment} superclass. * <p>The {@code Servlet}-related property sources are added as * {@link StubPropertySource stubs} at this stage, and will be * {@linkplain #initPropertySources(ServletContext, ServletConfig) fully initialized} * once the actual {@link ServletContext} object becomes available. * @see StandardEnvironment#customizePropertySources * @see org.springframework.core.env.AbstractEnvironment#customizePropertySources * @see ServletConfigPropertySource * @see ServletContextPropertySource * @see org.springframework.jndi.JndiPropertySource * @see org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#initPropertySources * @see #initPropertySources(ServletContext, ServletConfig) */ @Override protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) { propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)); propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)); if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) { propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)); } super.customizePropertySources(propertySources); }
SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME 也会出现在properties的前列【即web.xml中配置选项】
因此可以得出结论
commandLineArgs>servletContextInitParams>servletContextInitParams>jndiProperties>systemProperties>systemEnvironment>properties>defaultProperties
至于小伙伴认为为啥会defaultProperties排在最后
private void addConfigurationProperties( ConfigurationPropertySources configurationSources) { MutablePropertySources existingSources = this.environment .getPropertySources(); if (existingSources.contains(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES)) { existingSources.addBefore(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, configurationSources); } else { existingSources.addLast(configurationSources); } }



