- 线性回归
线性回归中的数学知识
在线性回归中,最重要的莫过于在一大堆的数据中找回归方程
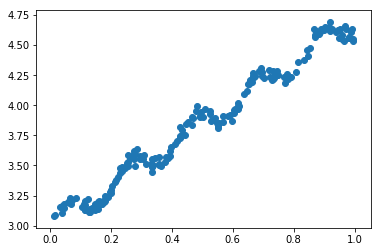
比较简单的方法是,可以利用最小二乘法寻找误差最小的那条直线.
利用最小二乘法计算loss可以写为:
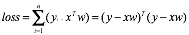
为了找到loss最小的那条直线,我们可以对w求导,得到
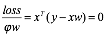
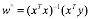
因此求回归方程转变为求参数w.
实现代码
def standRegres(xArr,yArr): xMat=np.mat(xArr) yMat=np.mat(yArr).T xTx=xMat.T*xMat if np.linalg.det(xTx)==0.0: print('error') return ws=xTx.I*(xMat.T*yMat) return ws
求出参数w
将回归直线去拟合实际数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(111) ax.scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0],yMat.T[:,0].flatten().A[0]) xCopy=xMat.copy() xCopy.sort(0) yHat=xCopy*ws ax.plot(xCopy[:,1],yHat) plt.show()
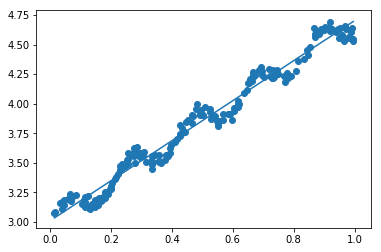
可以看到虽然直线显示了大概的趋势,但并不能很好的去拟合数据,下面介绍一种强大的回归--""局部加权线性回归"",可解决上面这个拟合度不够的问题.
2. 局部加权线性回归
局部加权线性回归中的数学知识
相对于线性回归 , 局部加权的意思是对于每一个特征 , 都给添加一个权重 , 然后基于普通的最小均方差来进行回归.
这里使用高斯核进行计算每一个点的权重
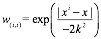
对于w^的计算和上面类似,只是添加了权重w
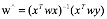
实现代码
def lwlr(testPoint,xArr,yArr,k=1.0): xMat=np.mat(xArr) yMat=np.mat(yArr).T m=np.shape(xMat)[0] weights=np.mat(np.eye((m))) for j in range(m): diffMat=testPoint-xMat[j,:] weights[j,j]=np.exp(diffMat*diffMat.T/(-2.0*k**2)) xTx=xMat.T*(weights*xMat) if np.linalg.det(xTx)==0.0: print("error") return ws=xTx.I*(xMat.T*(weights*yMat)) return testPoint*ws def lwlrTest(testArr,xArr,yArr,k=1.0): m=np.shape(testArr)[0] yHat=np.zeros(m) for i in range(m): yHat[i]=lwlr(testArr[i],xArr,yArr,k) return yHat
拟合效果
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(111) ax.plot(xSort[:,1],yHat[srtInd]) ax.scatter(xMat[:,1].flatten().A[0],np.mat(yArr).T.flatten().A[0],s=2,c='red') plt.show()
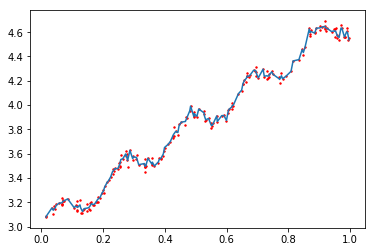
代码和数据均已上传到,有需要的朋友可以下载..
GitHub
码云




