前言
相信有并发经验的小伙伴对于ConcurrentHashMap不会陌生。
上一篇我们描述了cow容器 cow容器之CopyOnWriteArrayList,主要是CopyOnWriteArrayList,当然我们也有同步容器可以选择(Collections.synchronizedCollection等)
提到并发想必大家最常用的还是本篇的主角 ConcurrentHashMap
思路
提到并发,大家的思路无非就是加锁。那么我们可以考虑一下为啥需要加锁呢?存在竞态条件呗
那如何提高线程并发度呢?
一个现实生活中的例子就是银行多开几个窗口,那么自然可以把并发度提高。
我们考虑如下问
- 容器在读的时候不需要任何同步(因为数据未更新)
- 容器写完了之后其他线程读取或者再次写入必须要同步
- 如果用户操作的不同数据 可以不同步
- 如果用户操作的同一个数据 必须同步
在mysql中我们通常会有表级锁,行级锁也是同样的道理。
那么要求我们将并发度提升的关键在于锁的细化(锁分离)
关键就在于我们可以吧ConcurrentHashMap的并发粒度降低,并发冲突减小
源码
类图
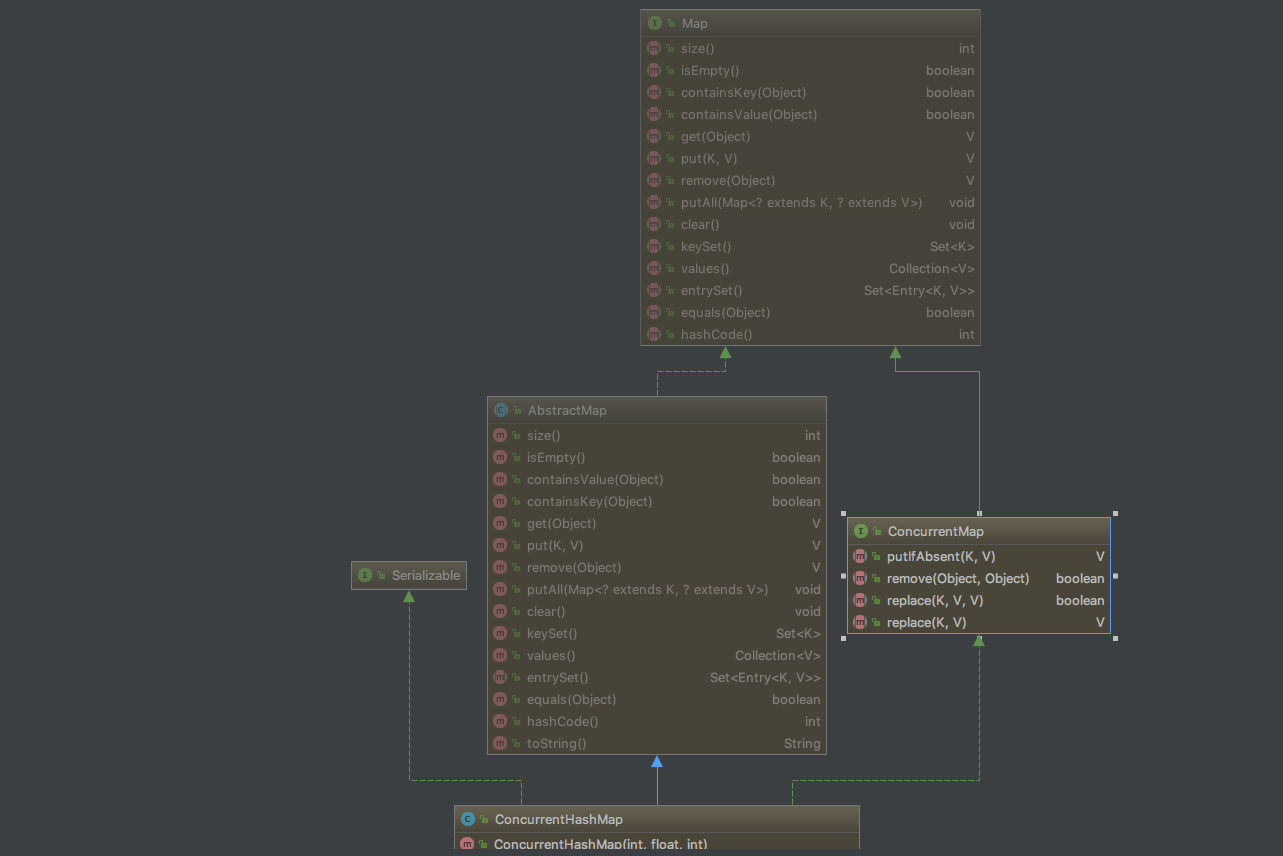
ConcurrentHashMap在实现了Map接口的基础上同时实现了ConcurrentMap接口
该接口提供了一系列等价原语
public interface ConcurrentMap<K, V> extends Map<K, V> { /** * If the specified key is not already associated * with a value, associate it with the given value. * This is equivalent to * <pre> * if (!map.containsKey(key)) * return map.put(key, value); * else * return map.get(key);</pre> * except that the action is performed atomically. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with the specified key, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for the key. * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with the key, * if the implementation supports null values.) * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>put</tt> operation * is not supported by this map * @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified key or value * prevents it from being stored in this map * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null, * and this map does not permit null keys or values * @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified key * or value prevents it from being stored in this map * */ V putIfAbsent(K key, V value); /** * Removes the entry for a key only if currently mapped to a given value. * This is equivalent to * <pre> * if (map.containsKey(key) && map.get(key).equals(value)) { * map.remove(key); * return true; * } else return false;</pre> * except that the action is performed atomically. * * @param key key with which the specified value is associated * @param value value expected to be associated with the specified key * @return <tt>true</tt> if the value was removed * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>remove</tt> operation * is not supported by this map * @throws ClassCastException if the key or value is of an inappropriate * type for this map * (<a href="../Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>) * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null, * and this map does not permit null keys or values * (<a href="../Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>) */ boolean remove(Object key, Object value); /** * Replaces the entry for a key only if currently mapped to a given value. * This is equivalent to * <pre> * if (map.containsKey(key) && map.get(key).equals(oldValue)) { * map.put(key, newValue); * return true; * } else return false;</pre> * except that the action is performed atomically. * * @param key key with which the specified value is associated * @param oldValue value expected to be associated with the specified key * @param newValue value to be associated with the specified key * @return <tt>true</tt> if the value was replaced * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>put</tt> operation * is not supported by this map * @throws ClassCastException if the class of a specified key or value * prevents it from being stored in this map * @throws NullPointerException if a specified key or value is null, * and this map does not permit null keys or values * @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of a specified key * or value prevents it from being stored in this map */ boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue); /** * Replaces the entry for a key only if currently mapped to some value. * This is equivalent to * <pre> * if (map.containsKey(key)) { * return map.put(key, value); * } else return null;</pre> * except that the action is performed atomically. * * @param key key with which the specified value is associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with the specified key, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for the key. * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with the key, * if the implementation supports null values.) * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>put</tt> operation * is not supported by this map * @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified key or value * prevents it from being stored in this map * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null, * and this map does not permit null keys or values * @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified key * or value prevents it from being stored in this map */ V replace(K key, V value);
构造函数
/** * Creates a new, empty map with the specified initial * capacity, load factor and concurrency level. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation * performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements. * @param loadFactor the load factor threshold, used to control resizing. * Resizing may be performed when the average number of elements per * bin exceeds this threshold. * @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently * updating threads. The implementation performs internal sizing * to try to accommodate this many threads. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is * negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are * nonpositive. */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; // Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments int sshift = 0; int ssize = 1; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1; } this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift; this.segmentMask = ssize - 1; if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1; // create segments and segments[0] Segment<K,V> s0 = new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor), (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]); Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize]; UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0] this.segments = ss; } /** * Creates a new, empty map with the specified initial capacity * and load factor and with the default concurrencyLevel (16). * * @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal * sizing to accommodate this many elements. * @param loadFactor the load factor threshold, used to control resizing. * Resizing may be performed when the average number of elements per * bin exceeds this threshold. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of * elements is negative or the load factor is nonpositive * * @since 1.6 */ public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL); } /** * Creates a new, empty map with the specified initial capacity, * and with default load factor (0.75) and concurrencyLevel (16). * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation * performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of * elements is negative. */ public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL); } /** * Creates a new, empty map with a default initial capacity (16), * load factor (0.75) and concurrencyLevel (16). */ public ConcurrentHashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL); }
通常情况下 我们会调用无参构造函数,那么意味着默认负载因子为0.75,默认初始容量16,默认并发度16(16个segment)
和HashMap原理相当相似,选择了power-of-two来作为相关参数。
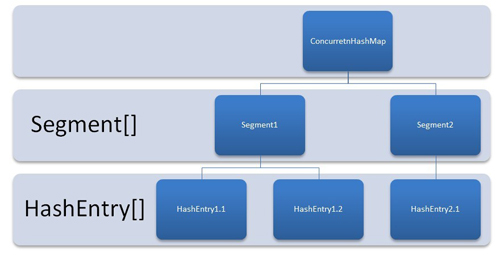
从原理图我们可以看到ConcurrentHashMap需要初始化一个Segment数组,同时真是的KV存放在对应的Segment中。
因此首先初始化Segment数组,细心的小伙伴可能注意到了
Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize]; UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0]
UNSAFE这个属于在Java中作弊器般的存在被用来做多种性能炸裂的基础库(比如netty等)需要注意的是Jdk9发布后该类的包名已经做了修改 这个后面可以探讨
/** * Segments are specialized versions of hash tables. This * subclasses from ReentrantLock opportunistically, just to * simplify some locking and avoid separate construction. */ static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable { /* * Segments maintain a table of entry lists that are always * kept in a consistent state, so can be read (via volatile * reads of segments and tables) without locking. This * requires replicating nodes when necessary during table * resizing, so the old lists can be traversed by readers * still using old version of table. * * This class defines only mutative methods requiring locking. * Except as noted, the methods of this class perform the * per-segment versions of ConcurrentHashMap methods. (Other * methods are integrated directly into ConcurrentHashMap * methods.) These mutative methods use a form of controlled * spinning on contention via methods scanAndLock and * scanAndLockForPut. These intersperse tryLocks with * traversals to locate nodes. The main benefit is to absorb * cache misses (which are very common for hash tables) while * obtaining locks so that traversal is faster once * acquired. We do not actually use the found nodes since they * must be re-acquired under lock anyway to ensure sequential * consistency of updates (and in any case may be undetectably * stale), but they will normally be much faster to re-locate. * Also, scanAndLockForPut speculatively creates a fresh node * to use in put if no node is found. */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L; /** * The maximum number of times to tryLock in a prescan before * possibly blocking on acquire in preparation for a locked * segment operation. On multiprocessors, using a bounded * number of retries maintains cache acquired while locating * nodes. */ static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1; /** * The per-segment table. Elements are accessed via * entryAt/setEntryAt providing volatile semantics. */ transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table; /** * The number of elements. Accessed only either within locks * or among other volatile reads that maintain visibility. */ transient int count; /** * The total number of mutative operations in this segment. * Even though this may overflows 32 bits, it provides * sufficient accuracy for stability checks in CHM isEmpty() * and size() methods. Accessed only either within locks or * among other volatile reads that maintain visibility. */ transient int modCount; /** * The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold. * (The value of this field is always <tt>(int)(capacity * * loadFactor)</tt>.) */ transient int threshold; /** * The load factor for the hash table. Even though this value * is same for all segments, it is replicated to avoid needing * links to outer object. * @serial */ final float loadFactor; Segment(float lf, int threshold, HashEntry<K,V>[] tab) { this.loadFactor = lf; this.threshold = threshold; this.table = tab; } final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); V oldValue; try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash; HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index); for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { if (e != null) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent) { e.value = value; ++modCount; } break; } e = e.next; } else { if (node != null) node.setNext(first); else node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first); int c = count + 1; if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) rehash(node); else setEntryAt(tab, index, node); ++modCount; count = c; oldValue = null; break; } } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue; } /** * Doubles size of table and repacks entries, also adding the * given node to new table */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void rehash(HashEntry<K,V> node) { /* * Reclassify nodes in each list to new table. Because we * are using power-of-two expansion, the elements from * each bin must either stay at same index, or move with a * power of two offset. We eliminate unnecessary node * creation by catching cases where old nodes can be * reused because their next fields won't change. * Statistically, at the default threshold, only about * one-sixth of them need cloning when a table * doubles. The nodes they replace will be garbage * collectable as soon as they are no longer referenced by * any reader thread that may be in the midst of * concurrently traversing table. Entry accesses use plain * array indexing because they are followed by volatile * table write. */ HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1; threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable = (HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity]; int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1; for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) { HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i]; if (e != null) { HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next; int idx = e.hash & sizeMask; if (next == null) // Single node on list newTable[idx] = e; else { // Reuse consecutive sequence at same slot HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e; int lastIdx = idx; for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next; last != null; last = last.next) { int k = last.hash & sizeMask; if (k != lastIdx) { lastIdx = k; lastRun = last; } } newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun; // Clone remaining nodes for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { V v = p.value; int h = p.hash; int k = h & sizeMask; HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k]; newTable[k] = new HashEntry<K,V>(h, p.key, v, n); } } } } int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; // add the new node node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]); newTable[nodeIndex] = node; table = newTable; } /** * Scans for a node containing given key while trying to * acquire lock, creating and returning one if not found. Upon * return, guarantees that lock is held. UNlike in most * methods, calls to method equals are not screened: Since * traversal speed doesn't matter, we might as well help warm * up the associated code and accesses as well. * * @return a new node if key not found, else null */ private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) { HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash); HashEntry<K,V> e = first; HashEntry<K,V> node = null; int retries = -1; // negative while locating node while (!tryLock()) { HashEntry<K,V> f; // to recheck first below if (retries < 0) { if (e == null) { if (node == null) // speculatively create node node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); retries = 0; } else if (key.equals(e.key)) retries = 0; else e = e.next; } else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) { lock(); break; } else if ((retries & 1) == 0 && (f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) { e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changed retries = -1; } } return node; } /** * Scans for a node containing the given key while trying to * acquire lock for a remove or replace operation. Upon * return, guarantees that lock is held. Note that we must * lock even if the key is not found, to ensure sequential * consistency of updates. */ private void scanAndLock(Object key, int hash) { // similar to but simpler than scanAndLockForPut HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash); HashEntry<K,V> e = first; int retries = -1; while (!tryLock()) { HashEntry<K,V> f; if (retries < 0) { if (e == null || key.equals(e.key)) retries = 0; else e = e.next; } else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) { lock(); break; } else if ((retries & 1) == 0 && (f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) { e = first = f; retries = -1; } } } /** * Remove; match on key only if value null, else match both. */ final V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) { if (!tryLock()) scanAndLock(key, hash); V oldValue = null; try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash; HashEntry<K,V> e = entryAt(tab, index); HashEntry<K,V> pred = null; while (e != null) { K k; HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { V v = e.value; if (value == null || value == v || value.equals(v)) { if (pred == null) setEntryAt(tab, index, next); else pred.setNext(next); ++modCount; --count; oldValue = v; } break; } pred = e; e = next; } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue; } final boolean replace(K key, int hash, V oldValue, V newValue) { if (!tryLock()) scanAndLock(key, hash); boolean replaced = false; try { HashEntry<K,V> e; for (e = entryForHash(this, hash); e != null; e = e.next) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { if (oldValue.equals(e.value)) { e.value = newValue; ++modCount; replaced = true; } break; } } } finally { unlock(); } return replaced; } final V replace(K key, int hash, V value) { if (!tryLock()) scanAndLock(key, hash); V oldValue = null; try { HashEntry<K,V> e; for (e = entryForHash(this, hash); e != null; e = e.next) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; ++modCount; break; } } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue; } final void clear() { lock(); try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; for (int i = 0; i < tab.length ; i++) setEntryAt(tab, i, null); ++modCount; count = 0; } finally { unlock(); } } }
此处需要注意Segment的超类是ReentrantLock 这是我们在做锁的时候经常用到的类。
存储KV的HashEntry
/** * ConcurrentHashMap list entry. Note that this is never exported * out as a user-visible Map.Entry. */ static final class HashEntry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEntry<K,V> next; HashEntry(int hash, K key, V value, HashEntry<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } /** * Sets next field with volatile write semantics. (See above * about use of putOrderedObject.) */ final void setNext(HashEntry<K,V> n) { UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, n); } // Unsafe mechanics static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; static final long nextOffset; static { try { UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class k = HashEntry.class; nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("next")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new Error(e); } } }
确实到处可见UNSAFE的使用
Hash
/** * Applies a supplemental hash function to a given hashCode, which * defends against poor quality hash functions. This is critical * because ConcurrentHashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, * that otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not * differ in lower or upper bits. */ private int hash(Object k) { int h = hashSeed; if ((0 != h) && (k instanceof String)) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h ^= k.hashCode(); // Spread bits to regularize both segment and index locations, // using variant of single-word Wang/Jenkins hash. h += (h << 15) ^ 0xffffcd7d; h ^= (h >>> 10); h += (h << 3); h ^= (h >>> 6); h += (h << 2) + (h << 14); return h ^ (h >>> 16); }
此处采用了jenkins hash http://blog.csdn.net/yueyedeai/article/details/17025265
从这里的hash算法明显比HashMap的hash复杂较多 ===》下文将利用该hash值做为定位segment和hashEntry的依据
put
/** * Maps the specified key to the specified value in this table. * Neither the key nor the value can be null. * * <p> The value can be retrieved by calling the <tt>get</tt> method * with a key that is equal to the original key. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt> * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public V put(K key, V value) { Segment<K,V> s; if (value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = hash(key); int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck (segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment s = ensureSegment(j); return s.put(key, hash, value, false); }
此处发现ConcurrentHashMap的value不支持null(这个后面分析)
同样其对应的key也不可以为null(hash方法不支持null)
首先需要定位一个正常的key放入到对应的Segment中将key计算出的hash值不带符号右移(hash >>> segmentShift) 该值在默认情况下为28 也就是将其右移28位【对于hash要求较高,最后几位必须尽可能的将元素分开】
// Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments int sshift = 0; int ssize = 1; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1; } this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift; this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;
这边还有依然是UNSAFE的小技巧
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck (segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment s = ensureSegment(j);
当找到对应的Segment后将KV放入Segment。
可以将此时的Segment当成原先的HashMap理解
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); V oldValue; try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash; HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index); for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { if (e != null) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent) { e.value = value; ++modCount; } break; } e = e.next; } else { if (node != null) node.setNext(first); else node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first); int c = count + 1; if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) rehash(node); else setEntryAt(tab, index, node); ++modCount; count = c; oldValue = null; break; } } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue; } /**
同样ConcurrentHashMap的构造函数中对于HashEntry的容量也做了计算,每个Segment的容量
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1; // create segments and segments[0] Segment<K,V> s0 = new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor), (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]); Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize];
那么默认情况下cap为2(MIN)
具体来看一下Segment的put方法
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); V oldValue; try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash; HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index); for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { if (e != null) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent) { e.value = value; ++modCount; } break; } e = e.next; } else { if (node != null) node.setNext(first); else node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first); int c = count + 1; if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) rehash(node); else setEntryAt(tab, index, node); ++modCount; count = c; oldValue = null; break; } } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue; }
由于Segment本身也是ReentrantLock 那么可以支持tryLock等方法。
首先尝试加锁(调用自身,只是针对本Segment,其他segment读写均不受影响),如果加锁不成功的话则在这期间可以找到需要放置的HashEntry的next指针(或者创建的HashEntry节点)
/** * Gets the table entry for the given segment and hash */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") static final <K,V> HashEntry<K,V> entryForHash(Segment<K,V> seg, int h) { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab; return (seg == null || (tab = seg.table) == null) ? null : (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile (tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE); } /** * Scans for a node containing given key while trying to * acquire lock, creating and returning one if not found. Upon * return, guarantees that lock is held. UNlike in most * methods, calls to method equals are not screened: Since * traversal speed doesn't matter, we might as well help warm * up the associated code and accesses as well. * * @return a new node if key not found, else null */ private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) { HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash); HashEntry<K,V> e = first; HashEntry<K,V> node = null; int retries = -1; // negative while locating node while (!tryLock()) { HashEntry<K,V> f; // to recheck first below if (retries < 0) { if (e == null) { if (node == null) // speculatively create node node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); retries = 0; } else if (key.equals(e.key)) retries = 0; else e = e.next; } else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) { lock(); break; } else if ((retries & 1) == 0 && (f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) { e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changed retries = -1; } } return node; }
根据hash值和当前的Segment的HashEntry的数组大小进行hash 找到对应的slot进行放置。期间自然也会有和HashMap一般的rehash(当count超过了阈值)
/** * Doubles size of table and repacks entries, also adding the * given node to new table */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void rehash(HashEntry<K,V> node) { /* * Reclassify nodes in each list to new table. Because we * are using power-of-two expansion, the elements from * each bin must either stay at same index, or move with a * power of two offset. We eliminate unnecessary node * creation by catching cases where old nodes can be * reused because their next fields won't change. * Statistically, at the default threshold, only about * one-sixth of them need cloning when a table * doubles. The nodes they replace will be garbage * collectable as soon as they are no longer referenced by * any reader thread that may be in the midst of * concurrently traversing table. Entry accesses use plain * array indexing because they are followed by volatile * table write. */ HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1; threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable = (HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity]; int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1; for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) { HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i]; if (e != null) { HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next; int idx = e.hash & sizeMask; if (next == null) // Single node on list newTable[idx] = e; else { // Reuse consecutive sequence at same slot HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e; int lastIdx = idx; for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next; last != null; last = last.next) { int k = last.hash & sizeMask; if (k != lastIdx) { lastIdx = k; lastRun = last; } } newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun; // Clone remaining nodes for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { V v = p.value; int h = p.hash; int k = h & sizeMask; HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k]; newTable[k] = new HashEntry<K,V>(h, p.key, v, n); } } } } int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; // add the new node node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]); newTable[nodeIndex] = node; table = newTable; }
基本上就是旧的Segment容量扩大至2倍(注意姿势扩充本Segment)那么其他的不会扩充,不会出现其他的锁的情况。
最终完成操作后需要释放lock
get
/** * Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, * or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key. * * <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key * {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)}, * then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns * {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.) * * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null */ public V get(Object key) { Segment<K,V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overhead HashEntry<K,V>[] tab; int h = hash(key); long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null && (tab = s.table) != null) { for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile (tab, ((long)(((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE); e != null; e = e.next) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k))) return e.value; } } return null; }
根据hash直接定位到Segment在定位到HashEntry进行拉链式寻找
remove
/** * Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this map. * This method does nothing if the key is not in the map. * * @param key the key that needs to be removed * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt> * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null */ public V remove(Object key) { int hash = hash(key); Segment<K,V> s = segmentForHash(hash); return s == null ? null : s.remove(key, hash, null); } /** * {@inheritDoc} * * @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null */ public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) { int hash = hash(key); Segment<K,V> s; return value != null && (s = segmentForHash(hash)) != null && s.remove(key, hash, value) != null; }
同样的道理找到对应的Segment做HashEntry的处理 区别在于提供了remove原子版本
* <pre> * if (map.containsKey(key) && map.get(key).equals(value)) { * map.remove(key); * return true; * } else return false;</pre>
size
由于采用了多个Segment管理此时无法直接获得ConcurrentHashMap的size
需要累计获取
/** * Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. If the * map contains more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns * <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>. * * @return the number of key-value mappings in this map */ public int size() { // Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to // continuous async changes in table, resort to locking. final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments; int size; boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bits long sum; // sum of modCounts long last = 0L; // previous sum int retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retry try { for (;;) { if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation } sum = 0L; size = 0; overflow = false; for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) { Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j); if (seg != null) { sum += seg.modCount; int c = seg.count; if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0) overflow = true; } } if (sum == last) break; last = sum; } } finally { if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) segmentAt(segments, j).unlock(); } } return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size; }
此处有个很有意思的操作。首先获取所有Segment的count之和。循环一次如果上次的结果和本次的结果相同则直接返回size(性能不错,可能大多数情况也能覆盖)
否则最多重复三次,当第三次仍然不相同,则开始加锁。当数据发生溢出的时候直接返回Integer.MAX_VALUE。
isEmpty
/** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains no key-value mappings. * * @return <tt>true</tt> if this map contains no key-value mappings */ public boolean isEmpty() { /* * Sum per-segment modCounts to avoid mis-reporting when * elements are concurrently added and removed in one segment * while checking another, in which case the table was never * actually empty at any point. (The sum ensures accuracy up * through at least 1<<31 per-segment modifications before * recheck.) Methods size() and containsValue() use similar * constructions for stability checks. */ long sum = 0L; final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments; for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) { Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j); if (seg != null) { if (seg.count != 0) return false; sum += seg.modCount; } } if (sum != 0L) { // recheck unless no modifications for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) { Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j); if (seg != null) { if (seg.count != 0) return false; sum -= seg.modCount; } } if (sum != 0L) return false; } return true; }
该方法没有了任何和锁相关的操作,因此性能OK。直接判断多个Segment有一个count不为0就直接返回false。
这也是强调集合的判断中判断是否为空不要使用size()!=0来,否则可能性能不佳(size可能要加锁)
iterator
abstract class HashIterator { int nextSegmentIndex; int nextTableIndex; HashEntry<K,V>[] currentTable; HashEntry<K, V> nextEntry; HashEntry<K, V> lastReturned; HashIterator() { nextSegmentIndex = segments.length - 1; nextTableIndex = -1; advance(); } /** * Set nextEntry to first node of next non-empty table * (in backwards order, to simplify checks). */ final void advance() { for (;;) { if (nextTableIndex >= 0) { if ((nextEntry = entryAt(currentTable, nextTableIndex--)) != null) break; } else if (nextSegmentIndex >= 0) { Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, nextSegmentIndex--); if (seg != null && (currentTable = seg.table) != null) nextTableIndex = currentTable.length - 1; } else break; } } final HashEntry<K,V> nextEntry() { HashEntry<K,V> e = nextEntry; if (e == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); lastReturned = e; // cannot assign until after null check if ((nextEntry = e.next) == null) advance(); return e; } public final boolean hasNext() { return nextEntry != null; } public final boolean hasMoreElements() { return nextEntry != null; } public final void remove() { if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); ConcurrentHashMap.this.remove(lastReturned.key); lastReturned = null; } } final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> { public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { return new EntryIterator(); } public boolean contains(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; V v = ConcurrentHashMap.this.get(e.getKey()); return v != null && v.equals(e.getValue()); } public boolean remove(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; return ConcurrentHashMap.this.remove(e.getKey(), e.getValue()); } public int size() { return ConcurrentHashMap.this.size(); } public boolean isEmpty() { return ConcurrentHashMap.this.isEmpty(); } public void clear() { ConcurrentHashMap.this.clear(); } }
核心在于其advance。查看注释也看到其是按照倒序进行遍历的,为了减少一些check(常用的技巧) 当判断是否存在元素(遍历是否结束时)
final HashEntry<K,V> nextEntry() { HashEntry<K,V> e = nextEntry; if (e == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); lastReturned = e; // cannot assign until after null check if ((nextEntry = e.next) == null) advance(); return e; } public final boolean hasNext() { return nextEntry != null; }
其中nextEntry是将获取当前table倒序遍历后的entry结果直到数据index<0
OK 我们回到为啥ConcurrentHashMap不可以放置null key
来自作者的解答 [concurrency-interest] Handling Null Values in ConcurrentHashMap
The main reason that nulls aren't allowed in ConcurrentMaps (ConcurrentHashMaps, ConcurrentSkipListMaps) is that ambiguities that may be just barely tolerable in non-concurrent maps can't be accommodated. The main one is that if map.get(key) returns null, you can't detect whether the key explicitly maps to null vs the key isn't mapped. In a non-concurrent map, you can check this via map.contains(key), but in a concurrent one, the map might have changed between calls.
参考
http://ifeve.com/concurrenthashmap/



