背景
前面几篇的队列基本都是和插入顺序相关的,一般来说可以先进先出,当然也可以通过双向队列实现进后出等等
那么在开发中还存在如下一些需求 不同的任务过来可以进入到不同的处理阶段【比如某些钱&库存相关的任务等等】
之前实现过redis下面的优先级队列 可以参考Redis实现优先级队列
现在来看看Java的优先级队列PriorityQueue
源码
类图
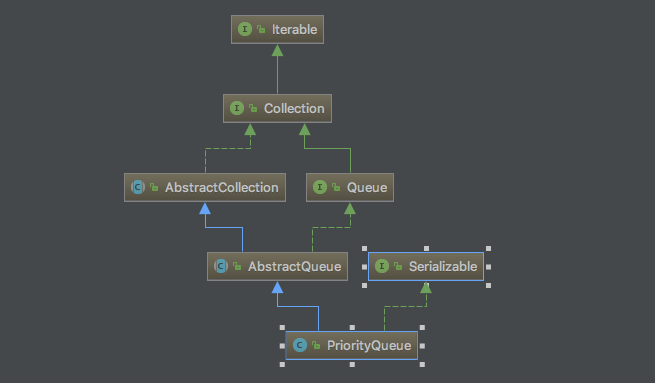
/** * An unbounded priority {@linkplain Queue queue} based on a priority heap. * The elements of the priority queue are ordered according to their * {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}, or by a {@link Comparator} * provided at queue construction time, depending on which constructor is * used. A priority queue does not permit {@code null} elements. * A priority queue relying on natural ordering also does not permit * insertion of non-comparable objects (doing so may result in * {@code ClassCastException}). * * <p>The <em>head</em> of this queue is the <em>least</em> element * with respect to the specified ordering. If multiple elements are * tied for least value, the head is one of those elements -- ties are * broken arbitrarily. The queue retrieval operations {@code poll}, * {@code remove}, {@code peek}, and {@code element} access the * element at the head of the queue. * * <p>A priority queue is unbounded, but has an internal * <i>capacity</i> governing the size of an array used to store the * elements on the queue. It is always at least as large as the queue * size. As elements are added to a priority queue, its capacity * grows automatically. The details of the growth policy are not * specified. * * <p>This class and its iterator implement all of the * <em>optional</em> methods of the {@link Collection} and {@link * Iterator} interfaces. The Iterator provided in method {@link * #iterator()} is <em>not</em> guaranteed to traverse the elements of * the priority queue in any particular order. If you need ordered * traversal, consider using {@code Arrays.sort(pq.toArray())}. * * <p> <strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong> * Multiple threads should not access a {@code PriorityQueue} * instance concurrently if any of the threads modifies the queue. * Instead, use the thread-safe {@link * java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue} class. * * <p>Implementation note: this implementation provides * O(log(n)) time for the enqueing and dequeing methods * ({@code offer}, {@code poll}, {@code remove()} and {@code add}); * linear time for the {@code remove(Object)} and {@code contains(Object)} * methods; and constant time for the retrieval methods * ({@code peek}, {@code element}, and {@code size}). * * <p>This class is a member of the * <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html"> * Java Collections Framework</a>. * * @since 1.5 * @author Josh Bloch, Doug Lea * @param <E> the type of elements held in this collection */
这是一个无界队列 利用了堆做排序算法。当插入的数据通过比较后越小就越先出队列。
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11; /** * Priority queue represented as a balanced binary heap: the two * children of queue[n] are queue[2*n+1] and queue[2*(n+1)]. The * priority queue is ordered by comparator, or by the elements' * natural ordering, if comparator is null: For each node n in the * heap and each descendant d of n, n <= d. The element with the * lowest value is in queue[0], assuming the queue is nonempty. */ private transient Object[] queue;
堆的两个字节点分别为 2*n和2*n+2
其虽然是无界队列但是默认初始容量为11(?)
构造函数
/** * Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the default initial * capacity (11) that orders its elements according to their * {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}. */ public PriorityQueue() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null); } /** * Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the specified initial * capacity that orders its elements according to their * {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering}. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity for this priority queue * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code initialCapacity} is less * than 1 */ public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, null); } /** * Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the specified initial capacity * that orders its elements according to the specified comparator. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity for this priority queue * @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this * priority queue. If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable * natural ordering} of the elements will be used. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code initialCapacity} is * less than 1 */ public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<? super E> comparator) { // Note: This restriction of at least one is not actually needed, // but continues for 1.5 compatibility if (initialCapacity < 1) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity]; this.comparator = comparator; }
这边很明显对于初始容量没有做任何计算【这个和HashMap等等都有区别】
offer
/** * Inserts the specified element into this priority queue. * * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer}) * @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be * compared with elements currently in this priority queue * according to the priority queue's ordering * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null */ public boolean offer(E e) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); modCount++; int i = size; if (i >= queue.length) grow(i + 1); size = i + 1; if (i == 0) queue[0] = e; else siftUp(i, e); return true; } /** * Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by * promoting x up the tree until it is greater than or equal to * its parent, or is the root. * * To simplify and speed up coercions and comparisons. the * Comparable and Comparator versions are separated into different * methods that are otherwise identical. (Similarly for siftDown.) * * @param k the position to fill * @param x the item to insert */ private void siftUp(int k, E x) { if (comparator != null) siftUpUsingComparator(k, x); else siftUpComparable(k, x); } private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x; while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; Object e = queue[parent]; if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0) break; queue[k] = e; k = parent; } queue[k] = key; } private void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, E x) { while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; Object e = queue[parent]; if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0) break; queue[k] = e; k = parent; } queue[k] = x; } /** * Increases the capacity of the array. * * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = queue.length; // Double size if small; else grow by 50% int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ? (oldCapacity + 2) : (oldCapacity >> 1)); // overflow-conscious code if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity); }
由于实现采用了数组结构 当放入元素是如果出现容量不够则需要扩容
扩容策略如下:
- 旧容量比64小则扩容为2倍+2[几乎就是2倍]
- 旧容量大于等于64则扩容为1.5倍
如果当队列里面没有元素则直接放入队列顶 否则需要进行排序操作
执行排序操作分两种:
- 使用比较器
- 使用自身实现的comparable
此时就是一个构建最小堆的过程
那么就是讲插入的元素和父亲元素进行比较直到最终到达顶部或者完成最小堆的构建
那么我们可以先找到其父亲节点。
PriorityQueue使用了如下的方式
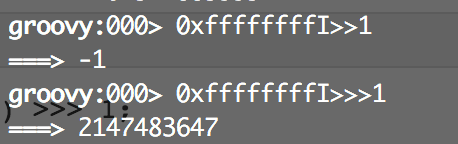
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
使用无符号右移进行完成 我们知道父亲节点的两个孩子节点分别为2*n+1和2*n+2 如果存在的话
那么正常我们实现的话可能就是 (k-1)/2 当然使用右移相对来说比除法更加效率~其次也考虑了使用无符号右移
比如
因此可以完成最小堆的构建
poll
public E poll() { if (size == 0) return null; int s = --size; modCount++; E result = (E) queue[0]; E x = (E) queue[s]; queue[s] = null; if (s != 0) siftDown(0, x); return result; } /** * Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by * demoting x down the tree repeatedly until it is less than or * equal to its children or is a leaf. * * @param k the position to fill * @param x the item to insert */ private void siftDown(int k, E x) { if (comparator != null) siftDownUsingComparator(k, x); else siftDownComparable(k, x); } private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x; int half = size >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least Object c = queue[child]; int right = child + 1; if (right < size && ((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0) c = queue[child = right]; if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0) break; queue[k] = c; k = child; } queue[k] = key; } private void siftDownUsingComparator(int k, E x) { int half = size >>> 1; while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1) + 1; Object c = queue[child]; int right = child + 1; if (right < size && comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0) c = queue[child = right]; if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0) break; queue[k] = c; k = child; } queue[k] = x; }
当需要出队列时直接把第一个元素弹出即可
以前课本里面的方案直接将最后一个元素放入到顶部即可
然后依次进行比较直到达成完全符合堆的特征。
但是由于Queue继承了Collection接口。该接口声明了remove(Object o)
因此删除的元素也有可能并非是顶部【事实上我们依然可以吧最后一个元素放到被删除的位置然后依次调整】
这边的策略是首先找到被删除节点的左孩子节点[当然如果被删除节点大于等于于队列长度的一半那么肯定已经不会有孩子了]
找到左孩子节点 如果存在对应的右孩子节点的节点的话 选择较小的作为父亲节点
iter
和我们设想的不一致的是用迭代器拿出来的结果不是有序的
private class Itr implements Iterator { int cursor = 0; List percolatedElems; int cursorPercolated = 0; int expectedModCount = modCount; int lastRet; Object lastRetPercolated; Itr() {} public boolean hasNext() { return cursor < size || percolatedElems != null; } public Object next() { checkForComodification(); if (cursor < size) { lastRet = cursor++; return buffer[lastRet]; } else if (percolatedElems != null) { lastRet = -1; lastRetPercolated = percolatedElems.remove(percolatedElems.size()-1); if (percolatedElems.isEmpty()) { percolatedElems = null; } return lastRetPercolated; } else { throw new NoSuchElementException(); } }
就是一个cursor直接向后移动 这一点要注意区别



