上篇描述了HashMap的数据结构原来你是这样的HashMap
本篇就TreeMap的实现进行详述
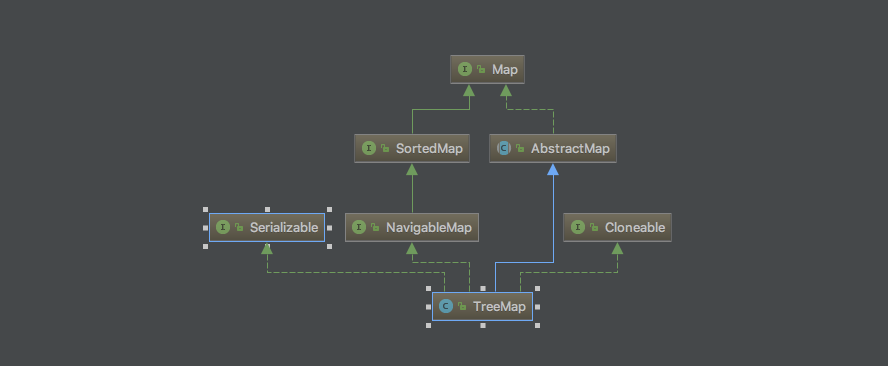
相比较HashMap其多了SortedMap(NavigableMap 类似ceil floor返回最接近的元素)接口实现
顾名思义就是支持了排序
说到排序可能大家就能想到一堆排序算法:堆排序 二分法 冒泡排序 插入排序 快排等等
那么TreeMap采用了红黑树来作为排序(传统的平衡二叉树指的是高度上的平衡一般称之为AVL树,即任意节点的左子树和右子数的高度相差不超过1,红黑树的是平衡指的是黑高度【BH】的的平衡,即任意节点到叶子节点的简单路径中黑色节点数目均相同)
几个常见的构造函数如下
/** * Constructs a new, empty tree map, using the natural ordering of its * keys. All keys inserted into the map must implement the {@link * Comparable} interface. Furthermore, all such keys must be * <em>mutually comparable</em>: {@code k1.compareTo(k2)} must not throw * a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys {@code k1} and * {@code k2} in the map. If the user attempts to put a key into the * map that violates this constraint (for example, the user attempts to * put a string key into a map whose keys are integers), the * {@code put(Object key, Object value)} call will throw a * {@code ClassCastException}. */ public TreeMap() { comparator = null; } /** * Constructs a new, empty tree map, ordered according to the given * comparator. All keys inserted into the map must be <em>mutually * comparable</em> by the given comparator: {@code comparator.compare(k1, * k2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys * {@code k1} and {@code k2} in the map. If the user attempts to put * a key into the map that violates this constraint, the {@code put(Object * key, Object value)} call will throw a * {@code ClassCastException}. * * @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this map. * If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable natural * ordering} of the keys will be used. */ public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; } /** * Constructs a new tree map containing the same mappings as the given * map, ordered according to the <em>natural ordering</em> of its keys. * All keys inserted into the new map must implement the {@link * Comparable} interface. Furthermore, all such keys must be * <em>mutually comparable</em>: {@code k1.compareTo(k2)} must not throw * a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys {@code k1} and * {@code k2} in the map. This method runs in n*log(n) time. * * @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map * @throws ClassCastException if the keys in m are not {@link Comparable}, * or are not mutually comparable * @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null */ public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = null; putAll(m); }
默认情况下comparator都是空,那么是如何进行排序的呢?
我们查看一下put方法
public V put(K key, V value) { Entry<K,V> t = root; if (t == null) { compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; } int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null) { do { parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } else { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; fixAfterInsertion(e); size++; modCount++; return null; }
看到compare方法
/** * Compares two keys using the correct comparison method for this TreeMap. */ final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) { return comparator==null ? ((Comparable<? super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2) : comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2); }
看来首先是使用comparator进行排序如果不存在则使用compareTo方法进行排序
那么必然如下问题:
- TreeMap可否使用key为null
- TreeMap的key是否Comparable之类
- 如果comparator发生了变化是否排序会受到影响需要resort?
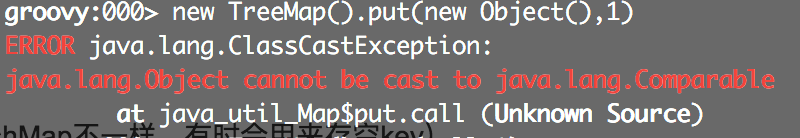
问题1. 当comparator为空的时候放入空key必然会导致npe发生(和hashMap不一样,有时会用来存空key)
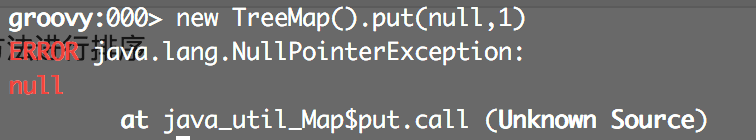
问题2:默认情况下如果放入了不支持排序的类型会导致强转类型失败
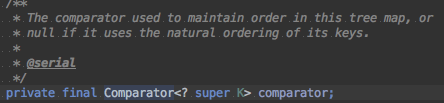
问题3:所以TreeMap将comparator设置为final那么该值必然只能设置一次
因此在通常场景下TreeMap的key还是需要校验是否为空(和HashMap不一样,当然是用comparator并且comparator支持null的话是OK的)
其实上述描述存在问题,事实上comparator方法不支持compare的参数为空 其详细约定如果为null要抛出npe
/** * Compares its two arguments for order. Returns a negative integer, * zero, or a positive integer as the first argument is less than, equal * to, or greater than the second.<p> * * In the foregoing description, the notation * <tt>sgn(</tt><i>expression</i><tt>)</tt> designates the mathematical * <i>signum</i> function, which is defined to return one of <tt>-1</tt>, * <tt>0</tt>, or <tt>1</tt> according to whether the value of * <i>expression</i> is negative, zero or positive.<p> * * The implementor must ensure that <tt>sgn(compare(x, y)) == * -sgn(compare(y, x))</tt> for all <tt>x</tt> and <tt>y</tt>. (This * implies that <tt>compare(x, y)</tt> must throw an exception if and only * if <tt>compare(y, x)</tt> throws an exception.)<p> * * The implementor must also ensure that the relation is transitive: * <tt>((compare(x, y)>0) && (compare(y, z)>0))</tt> implies * <tt>compare(x, z)>0</tt>.<p> * * Finally, the implementor must ensure that <tt>compare(x, y)==0</tt> * implies that <tt>sgn(compare(x, z))==sgn(compare(y, z))</tt> for all * <tt>z</tt>.<p> * * It is generally the case, but <i>not</i> strictly required that * <tt>(compare(x, y)==0) == (x.equals(y))</tt>. Generally speaking, * any comparator that violates this condition should clearly indicate * this fact. The recommended language is "Note: this comparator * imposes orderings that are inconsistent with equals." * * @param o1 the first object to be compared. * @param o2 the second object to be compared. * @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the * first argument is less than, equal to, or greater than the * second. * @throws NullPointerException if an argument is null and this * comparator does not permit null arguments * @throws ClassCastException if the arguments' types prevent them from * being compared by this comparator. */ int compare(T o1, T o2);
理论上都不支持null key
让我们重新来走一遍TreeMap的put过程。
这是一个典型的二叉查找树的查找与插入过程。
-
如果当树本身不存在的情况下直接将本身放入根并返回空
Entry<K,V> t = root; if (t == null) { compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; }
2.当树根存在直接按照排序查找到指定的节点(左孩子必然小于本身 右孩子必然大于本身 不支持相同大小,也就是当大小相同直接替换并返回old value)
int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null) { do { parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } else { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e;
3. 如果这是一根平衡二叉树那么由于数据的插入很可能导致失衡,那么可能需要一系列的旋转来完成二叉树的平衡(平衡的目的在于更好的查找速度)
大学里面可能都学过AVL树其实就是一种典型的平衡二叉树的实现(但是avl的旋转次数可能较多,导致整体统计性能不如红黑树)
在插入新的节点之后首先要做的就是重新平衡(旋转或者着色)
fixAfterInsertion(e);
/** From CLR */ private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) { if (p != null) { Entry<K,V> r = p.right; p.right = r.left; if (r.left != null) r.left.parent = p; r.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = r; else if (p.parent.left == p) p.parent.left = r; else p.parent.right = r; r.left = p; p.parent = r; } } /** From CLR */ private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) { if (p != null) { Entry<K,V> l = p.left; p.left = l.right; if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p; l.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = l; else if (p.parent.right == p) p.parent.right = l; else p.parent.left = l; l.right = p; p.parent = l; } } /** From CLR */ private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) { x.color = RED; while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) { if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) { Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); } else { if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); rotateLeft(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } else { Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); } else { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); rotateRight(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } } root.color = BLACK; }
这边首先描述一下红黑树的定义
除了二叉树的基本要求外,红黑树必须满足以下几点性质。
- 节点必须是红色或者黑色。
- 根节点必须是黑色。
- 叶节点(NIL)是黑色的。(NIL节点无数据,是空节点)
- 红色节点必须有两个黑色儿子节点。
- 从任一节点出发到其每个叶子节点的路径,黑色节点的数量是相等的。
先查看一下节点的定义
/** * Node in the Tree. Doubles as a means to pass key-value pairs back to * user (see Map.Entry). */ static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { K key; V value; Entry<K,V> left = null; Entry<K,V> right = null; Entry<K,V> parent; boolean color = BLACK; /** * Make a new cell with given key, value, and parent, and with * {@code null} child links, and BLACK color. */ Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.parent = parent; } /** * Returns the key. * * @return the key */ public K getKey() { return key; } /** * Returns the value associated with the key. * * @return the value associated with the key */ public V getValue() { return value; } /** * Replaces the value currently associated with the key with the given * value. * * @return the value associated with the key before this method was * called */ public V setValue(V value) { V oldValue = this.value; this.value = value; return oldValue; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue()); } public int hashCode() { int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()); int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); return keyHash ^ valueHash; } public String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } }
左旋操作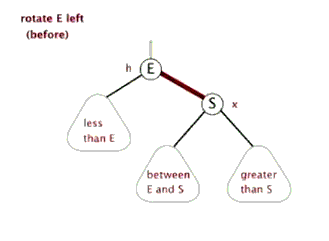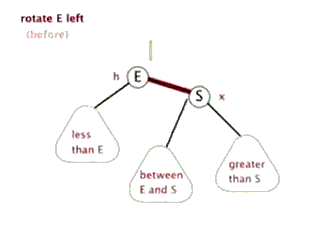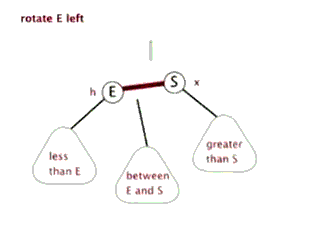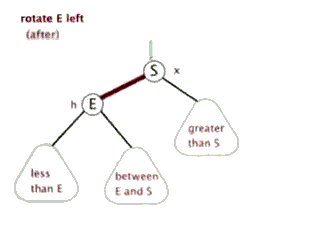
右旋操作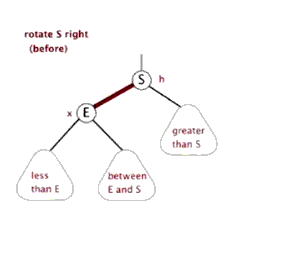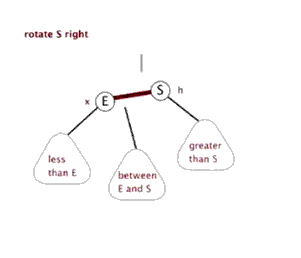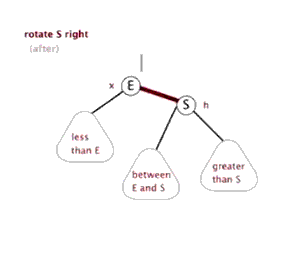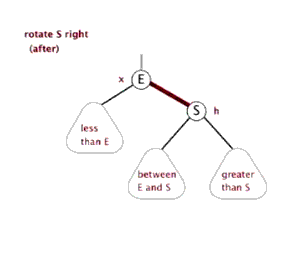
那么分几个场景来讨论插入:【默认孩子节点都是红色,设想如果颜色为黑色那么破坏了第五条特性,那么造成的旋转次数可能较多,实现相对困难】
- 当父亲节点是黑色,那么无需操作,直接插入新的红色孩子节点(不会破坏属性)
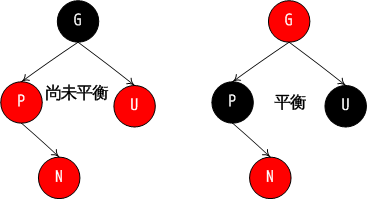
- 当父亲节点为红色(此时必然会破坏第4条特性)【以下操作均需要注意叔叔节点或者祖父节点均有可能不存在】===》当然此时祖父节点必然存在因为根节点必须为黑色
以父亲为左孩子为例,其余镜像即可 - 当叔叔节点为红色,此时将父亲节点和叔叔节点涂成黑色,同时将祖父节点涂成红色,并将当前指针指向祖父节点
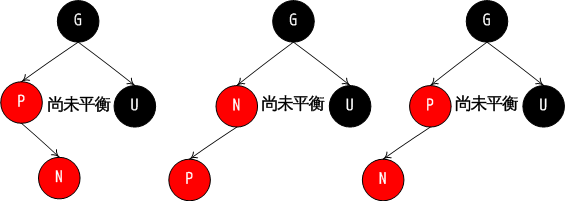
- 当叔叔节点为黑色,当前节点为父亲节点的右孩子 此时以父亲节点进行左旋 并将当前指针指向原父亲节点
- 当叔叔节点为黑色,当前节点为父亲节点左孩子 那么需要以父亲节点右旋 同时将父亲节点涂黑 原祖父节点涂红
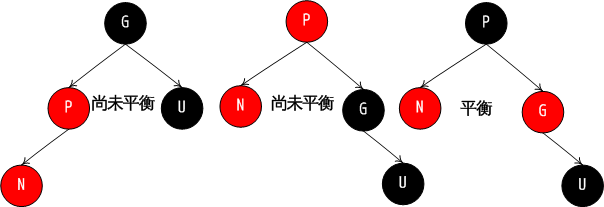
考虑一下左旋或者右旋的情况,事实上为了高度尽可能的低(最好是完美平衡二叉树)那么当新加的节点是左孩子自然要进行右旋(这样高度相应降低)右孩子自然进行左旋【这也是常规思路】 其余分情况进行颜色变更
那么从代码分析
/** From CLR */ private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) { x.color = RED; while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) { if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) { //父亲节点为祖父节点的左孩子节点 Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { //父亲节点和叔叔节点均为红色 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); //对应情况A } else { //父亲节点为红色和叔叔节点为黑色 if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) { //自身是父亲节点的右孩子 左旋父亲 指针并指向父亲节点 x = parentOf(x); rotateLeft(x); //对应情况B } //此时指针已经变成原父亲节点 逻辑走到情况C 所以此时的叔叔节点并未发生变化 因此叔叔节点仍然为黑色 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); //父亲涂红色 祖父涂黑色 父亲右旋 对应情况C } } else { //父亲节点为祖父节点的右孩子节点 Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { //父亲节点和叔叔节点均为红色 setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); //对应情况A } else { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { //自身是父亲节点的左孩子 右旋父亲 指针并指向父亲节点 x = parentOf(x); rotateRight(x); //对应情况B } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x))); //父亲涂黑色 祖父涂红色 父亲左旋 对应情况C } } } root.color = BLACK; //根节点必须为黑色 }
参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/hilow/p/3949188.html
http://blog.csdn.net/chenssy/article/details/26668941
http://www.cnblogs.com/daoluanxiaozi/p/3340382.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24795143?refer=dreawer
http://www.cnblogs.com/yangecnu/p/Introduce-Red-Black-Tree.html










