前言
在上文Nginx+Tomcat关于Session的管理中简单介绍了如何使用redis来集中管理session,本文首先将介绍默认的管理器是如何管理Session的生命周期的,然后在此基础上对Redis集中式管理Session进行分析。
Tomcat Manager介绍
上文中在Tomcat的context.xml中配置了Session管理器RedisSessionManager,实现了通过redis来存储session的功能;Tomcat本身提供了多种Session管理器,如下类图:
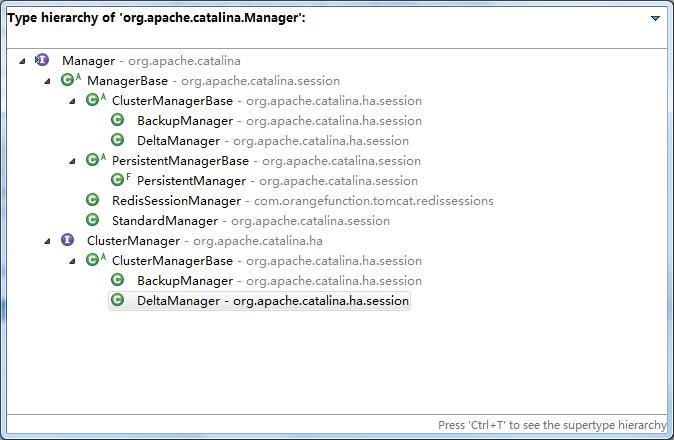
1.Manager接口类
定义了用来管理session的基本接口,包括:createSession,findSession,add,remove等对session操作的方法;还有getMaxActive,setMaxActive,getActiveSessions活跃会话的管理;还有Session有效期的接口;以及与Container相关联的接口;
2.ManagerBase抽象类
实现了Manager接口,提供了基本的功能,使用ConcurrentHashMap存放session,提供了对session的create,find,add,remove功能,并且在createSession中了使用类SessionIdGenerator来生成会话id,作为session的唯一标识;
3.ClusterManager接口类
实现了Manager接口,集群session的管理器,Tomcat内置的集群服务器之间的session复制功能;
4.ClusterManagerBase抽象类
继承了ManagerBase抽象类,实现ClusterManager接口类,实现session复制基本功能;
5.PersistentManagerBase抽象类
继承了ManagerBase抽象类,实现了session管理器持久化的基本功能;内部有一个Store存储类,具体实现有:FileStore和JDBCStore;
6.StandardManager类
继承ManagerBase抽象类,Tomcat默认的Session管理器(单机版);对session提供了持久化功能,tomcat关闭的时候会将session保存到javax.servlet.context.tempdir路径下的SESSIONS.ser文件中,启动的时候会从此文件中加载session;
7.PersistentManager类
继承PersistentManagerBase抽象类,如果session空闲时间过长,将空闲session转换为存储,所以在findsession时会首先从内存中获取session,获取不到会多一步到store中获取,这也是PersistentManager类和StandardManager类的区别;
8.DeltaManager类
继承ClusterManagerBase,每一个节点session发生变更(增删改),都会通知其他所有节点,其他所有节点进行更新操作,任何一个session在每个节点都有备份;
9.BackupManager类
继承ClusterManagerBase,会话数据只有一个备份节点,这个备份节点的位置集群中所有节点都可见;相比较DeltaManager数据传输量较小,当集群规模比较大时DeltaManager的数据传输量会非常大;
10.RedisSessionManager类
继承ManagerBase抽象类,非Tomcat内置的管理器,使用redis集中存储session,省去了节点之间的session复制,依赖redis的可靠性,比起sessin复制扩展性更好;
Session的生命周期
1.解析获取requestedSessionId
当我们在类中通过request.getSession()时,tomcat是如何处理的,可以查看Request中的doGetSession方法:
protected Session doGetSession(boolean create) { // There cannot be a session if no context has been assigned yet Context context = getContext(); if (context == null) { return (null); } // Return the current session if it exists and is valid if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) { session = null; } if (session != null) { return (session); } // Return the requested session if it exists and is valid Manager manager = context.getManager(); if (manager == null) { return null; // Sessions are not supported } if (requestedSessionId != null) { try { session = manager.findSession(requestedSessionId); } catch (IOException e) { session = null; } if ((session != null) && !session.isValid()) { session = null; } if (session != null) { session.access(); return (session); } } // Create a new session if requested and the response is not committed if (!create) { return (null); } if ((response != null) && context.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes(). contains(SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE) && response.getResponse().isCommitted()) { throw new IllegalStateException (sm.getString("coyoteRequest.sessionCreateCommitted")); } // Re-use session IDs provided by the client in very limited // circumstances. String sessionId = getRequestedSessionId(); if (requestedSessionSSL) { // If the session ID has been obtained from the SSL handshake then // use it. } else if (("/".equals(context.getSessionCookiePath()) && isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie())) { /* This is the common(ish) use case: using the same session ID with * multiple web applications on the same host. Typically this is * used by Portlet implementations. It only works if sessions are * tracked via cookies. The cookie must have a path of "/" else it * won't be provided for requests to all web applications. * * Any session ID provided by the client should be for a session * that already exists somewhere on the host. Check if the context * is configured for this to be confirmed. */ if (context.getValidateClientProvidedNewSessionId()) { boolean found = false; for (Container container : getHost().findChildren()) { Manager m = ((Context) container).getManager(); if (m != null) { try { if (m.findSession(sessionId) != null) { found = true; break; } } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore. Problems with this manager will be // handled elsewhere. } } } if (!found) { sessionId = null; } } } else { sessionId = null; } session = manager.createSession(sessionId); // Creating a new session cookie based on that session if ((session != null) && (getContext() != null) && getContext().getServletContext(). getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains( SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE)) { Cookie cookie = ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.createSessionCookie( context, session.getIdInternal(), isSecure()); response.addSessionCookieInternal(cookie); } if (session == null) { return null; } session.access(); return session; }
如果session已经存在,则直接返回;如果不存在则判定requestedSessionId是否为空,如果不为空则通过requestedSessionId到Session manager中获取session,如果为空,并且不是创建session操作,直接返回null;否则会调用Session manager创建一个新的session;
关于requestedSessionId是如何获取的,Tomcat内部可以支持从cookie和url中获取,具体可以查看CoyoteAdapter类的postParseRequest方法部分代码:
String sessionID; if (request.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes() .contains(SessionTrackingMode.URL)) { // Get the session ID if there was one sessionID = request.getPathParameter( SessionConfig.getSessionUriParamName( request.getContext())); if (sessionID != null) { request.setRequestedSessionId(sessionID); request.setRequestedSessionURL(true); } } // Look for session ID in cookies and SSL session parseSessionCookiesId(req, request);
可以发现首先去url解析sessionId,如果获取不到则去cookie中获取,此处的SessionUriParamName=jsessionid;在cookie被浏览器禁用的情况下,我们可以看到url后面跟着参数jsessionid=xxxxxx;下面看一下parseSessionCookiesId方法:
String sessionCookieName = SessionConfig.getSessionCookieName(context); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { ServerCookie scookie = serverCookies.getCookie(i); if (scookie.getName().equals(sessionCookieName)) { // Override anything requested in the URL if (!request.isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie()) { // Accept only the first session id cookie convertMB(scookie.getValue()); request.setRequestedSessionId (scookie.getValue().toString()); request.setRequestedSessionCookie(true); request.setRequestedSessionURL(false); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(" Requested cookie session id is " + request.getRequestedSessionId()); } } else { if (!request.isRequestedSessionIdValid()) { // Replace the session id until one is valid convertMB(scookie.getValue()); request.setRequestedSessionId (scookie.getValue().toString()); } } } }
sessionCookieName也是jsessionid,然后遍历cookie,从里面找出name=jsessionid的值赋值给request的requestedSessionId属性;
2.findSession查询session
获取到requestedSessionId之后,会通过此id去session Manager中获取session,不同的管理器获取的方式不一样,已默认的StandardManager为例:
protected Map<String, Session> sessions = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Session>(); public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException { if (id == null) { return null; } return sessions.get(id); }
3.createSession创建session
没有获取到session,指定了create=true,则创建session,已默认的StandardManager为例:
public Session createSession(String sessionId) { if ((maxActiveSessions >= 0) && (getActiveSessions() >= maxActiveSessions)) { rejectedSessions++; throw new TooManyActiveSessionsException( sm.getString("managerBase.createSession.ise"), maxActiveSessions); } // Recycle or create a Session instance Session session = createEmptySession(); // Initialize the properties of the new session and return it session.setNew(true); session.setValid(true); session.setCreationTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); session.setMaxInactiveInterval(((Context) getContainer()).getSessionTimeout() * 60); String id = sessionId; if (id == null) { id = generateSessionId(); } session.setId(id); sessionCounter++; SessionTiming timing = new SessionTiming(session.getCreationTime(), 0); synchronized (sessionCreationTiming) { sessionCreationTiming.add(timing); sessionCreationTiming.poll(); } return (session); }
如果传的sessionId为空,tomcat会生成一个唯一的sessionId,具体可以参考类StandardSessionIdGenerator的generateSessionId方法;这里发现创建完session之后并没有把session放入ConcurrentHashMap中,其实在session.setId(id)中处理了,具体代码如下:
public void setId(String id, boolean notify) { if ((this.id != null) && (manager != null)) manager.remove(this); this.id = id; if (manager != null) manager.add(this); if (notify) { tellNew(); } }
4.销毁Session
Tomcat会定期检测出不活跃的session,然后将其删除,一方面session占用内存,另一方面是安全性的考虑;启动tomcat的同时会启动一个后台线程用来检测过期的session,具体可以查看ContainerBase的内部类ContainerBackgroundProcessor:
protected class ContainerBackgroundProcessor implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { Throwable t = null; String unexpectedDeathMessage = sm.getString( "containerBase.backgroundProcess.unexpectedThreadDeath", Thread.currentThread().getName()); try { while (!threadDone) { try { Thread.sleep(backgroundProcessorDelay * 1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // Ignore } if (!threadDone) { Container parent = (Container) getMappingObject(); ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (parent.getLoader() != null) { cl = parent.getLoader().getClassLoader(); } processChildren(parent, cl); } } } catch (RuntimeException e) { t = e; throw e; } catch (Error e) { t = e; throw e; } finally { if (!threadDone) { log.error(unexpectedDeathMessage, t); } } } protected void processChildren(Container container, ClassLoader cl) { try { if (container.getLoader() != null) { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader (container.getLoader().getClassLoader()); } container.backgroundProcess(); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error("Exception invoking periodic operation: ", t); } finally { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl); } Container[] children = container.findChildren(); for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) { if (children[i].getBackgroundProcessorDelay() <= 0) { processChildren(children[i], cl); } } } }
backgroundProcessorDelay默认值是10,也就是每10秒检测一次,然后调用Container的backgroundProcess方法,此方法又调用Manager里面的backgroundProcess:
public void backgroundProcess() { count = (count + 1) % processExpiresFrequency; if (count == 0) processExpires(); } /** * Invalidate all sessions that have expired. */ public void processExpires() { long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis(); Session sessions[] = findSessions(); int expireHere = 0 ; if(log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Start expire sessions " + getName() + " at " + timeNow + " sessioncount " + sessions.length); for (int i = 0; i < sessions.length; i++) { if (sessions[i]!=null && !sessions[i].isValid()) { expireHere++; } } long timeEnd = System.currentTimeMillis(); if(log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("End expire sessions " + getName() + " processingTime " + (timeEnd - timeNow) + " expired sessions: " + expireHere); processingTime += ( timeEnd - timeNow ); }
processExpiresFrequency默认值是6,那其实最后就是6*10=60秒执行一次processExpires,具体如何检测过期在session的isValid方法中:
public boolean isValid() { if (!this.isValid) { return false; } if (this.expiring) { return true; } if (ACTIVITY_CHECK && accessCount.get() > 0) { return true; } if (maxInactiveInterval > 0) { long timeNow = System.currentTimeMillis(); int timeIdle; if (LAST_ACCESS_AT_START) { timeIdle = (int) ((timeNow - lastAccessedTime) / 1000L); } else { timeIdle = (int) ((timeNow - thisAccessedTime) / 1000L); } if (timeIdle >= maxInactiveInterval) { expire(true); } } return this.isValid; }
主要是通过对比当前时间到上次活跃的时间是否超过了maxInactiveInterval,如果超过了就做expire处理;
Redis集中式管理Session分析
在上文中使用tomcat-redis-session-manager来管理session,下面来分析一下是如果通过redis来集中式管理Session的;围绕session如何获取,如何创建,何时更新到redis,以及何时被移除;
1.如何获取
RedisSessionManager重写了findSession方法
public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException { RedisSession session = null; if (null == id) { currentSessionIsPersisted.set(false); currentSession.set(null); currentSessionSerializationMetadata.set(null); currentSessionId.set(null); } else if (id.equals(currentSessionId.get())) { session = currentSession.get(); } else { byte[] data = loadSessionDataFromRedis(id); if (data != null) { DeserializedSessionContainer container = sessionFromSerializedData(id, data); session = container.session; currentSession.set(session); currentSessionSerializationMetadata.set(container.metadata); currentSessionIsPersisted.set(true); currentSessionId.set(id); } else { currentSessionIsPersisted.set(false); currentSession.set(null); currentSessionSerializationMetadata.set(null); currentSessionId.set(null); } }
sessionId不为空的情况下,会先比较sessionId是否等于currentSessionId中的sessionId,如果等于则从currentSession中取出session,currentSessionId和currentSession都是ThreadLocal变量,这里并没有直接从redis里面取数据,如果同一线程没有去处理其他用户信息,是可以直接从内存中取出的,提高了性能;最后才从redis里面获取数据,从redis里面获取的是一段二进制数据,需要进行反序列化操作,相关序列化和反序列化都在JavaSerializer类中:
public void deserializeInto(byte[] data, RedisSession session, SessionSerializationMetadata metadata) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(data)); Throwable arg4 = null; try { CustomObjectInputStream x2 = new CustomObjectInputStream(bis, this.loader); Throwable arg6 = null; try { SessionSerializationMetadata x21 = (SessionSerializationMetadata) x2.readObject(); metadata.copyFieldsFrom(x21); session.readObjectData(x2); } catch (Throwable arg29) { ...... }
二进制数据中保存了2个对象,分别是SessionSerializationMetadata和RedisSession,SessionSerializationMetadata里面保存的是Session中的attributes信息,RedisSession其实也有attributes数据,相当于这份数据保存了2份;
2.如何创建
同样RedisSessionManager重写了createSession方法,2个重要的点分别:sessionId的唯一性问题和session保存到redis中;
// Ensure generation of a unique session identifier. if (null != requestedSessionId) { sessionId = sessionIdWithJvmRoute(requestedSessionId, jvmRoute); if (jedis.setnx(sessionId.getBytes(), NULL_SESSION) == 0L) { sessionId = null; } } else { do { sessionId = sessionIdWithJvmRoute(generateSessionId(), jvmRoute); } while (jedis.setnx(sessionId.getBytes(), NULL_SESSION) == 0L); // 1 = key set; 0 = key already existed }
分布式环境下有可能出现生成的sessionId相同的情况,所以需要确保唯一性;保存session到redis中是最核心的一个方法,何时更新,何时过期都在此方法中处理;
3.何时更新到redis
具体看saveInternal方法
protected boolean saveInternal(Jedis jedis, Session session, boolean forceSave) throws IOException { Boolean error = true; try { log.trace("Saving session " + session + " into Redis"); RedisSession redisSession = (RedisSession)session; if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Session Contents [" + redisSession.getId() + "]:"); Enumeration en = redisSession.getAttributeNames(); while(en.hasMoreElements()) { log.trace(" " + en.nextElement()); } } byte[] binaryId = redisSession.getId().getBytes(); Boolean isCurrentSessionPersisted; SessionSerializationMetadata sessionSerializationMetadata = currentSessionSerializationMetadata.get(); byte[] originalSessionAttributesHash = sessionSerializationMetadata.getSessionAttributesHash(); byte[] sessionAttributesHash = null; if ( forceSave || redisSession.isDirty() || null == (isCurrentSessionPersisted = this.currentSessionIsPersisted.get()) || !isCurrentSessionPersisted || !Arrays.equals(originalSessionAttributesHash, (sessionAttributesHash = serializer.attributesHashFrom(redisSession))) ) { log.trace("Save was determined to be necessary"); if (null == sessionAttributesHash) { sessionAttributesHash = serializer.attributesHashFrom(redisSession); } SessionSerializationMetadata updatedSerializationMetadata = new SessionSerializationMetadata(); updatedSerializationMetadata.setSessionAttributesHash(sessionAttributesHash); jedis.set(binaryId, serializer.serializeFrom(redisSession, updatedSerializationMetadata)); redisSession.resetDirtyTracking(); currentSessionSerializationMetadata.set(updatedSerializationMetadata); currentSessionIsPersisted.set(true); } else { log.trace("Save was determined to be unnecessary"); } log.trace("Setting expire timeout on session [" + redisSession.getId() + "] to " + getMaxInactiveInterval()); jedis.expire(binaryId, getMaxInactiveInterval()); error = false; return error; } catch (IOException e) { log.error(e.getMessage()); throw e; } finally { return error; } }
以上方法中大致有5中情况下需要保存数据到redis中,分别是:forceSave,redisSession.isDirty(),null == (isCurrentSessionPersisted = this.currentSessionIsPersisted.get()),!isCurrentSessionPersisted以及!Arrays.equals(originalSessionAttributesHash, (sessionAttributesHash = serializer.attributesHashFrom(redisSession)))其中一个为true的情况下保存数据到reids中;
3.1重点看一下forceSave,可以理解forceSave就是内置保存策略的一个标识,提供了三种内置保存策略:DEFAULT,SAVE_ON_CHANGE,ALWAYS_SAVE_AFTER_REQUEST
DEFAULT:默认保存策略,依赖其他四种情况保存session,
SAVE_ON_CHANGE:每次session.setAttribute()、session.removeAttribute()触发都会保存,
ALWAYS_SAVE_AFTER_REQUEST:每一个request请求后都强制保存,无论是否检测到变化;
3.2redisSession.isDirty()检测session内部是否有脏数据
public Boolean isDirty() { return Boolean.valueOf(this.dirty.booleanValue() || !this.changedAttributes.isEmpty()); }
每一个request请求后检测是否有脏数据,有脏数据才保存,实时性没有SAVE_ON_CHANGE高,但是也没有ALWAYS_SAVE_AFTER_REQUEST来的粗暴;
3.3后面三种情况都是用来检测三个ThreadLocal变量;
4.何时被移除
上一节中介绍了Tomcat内置看定期检测session是否过期,ManagerBase中提供了processExpires方法来处理session过去的问题,但是在RedisSessionManager重写了此方法
public void processExpires() { }
直接不做处理了,具体是利用了redis的设置生存时间功能,具体在saveInternal方法中:
jedis.expire(binaryId, getMaxInactiveInterval());
总结
本文大致分析了Tomcat Session管理器,以及tomcat-redis-session-manager是如何进行session集中式管理的,但是此工具完全依赖tomcat容器,如果想完全独立于应用服务器的方案,Spring session是一个不错的选择。


