背景
今天在查看Sonar的时候发现小伙伴在某些场景下如下使用
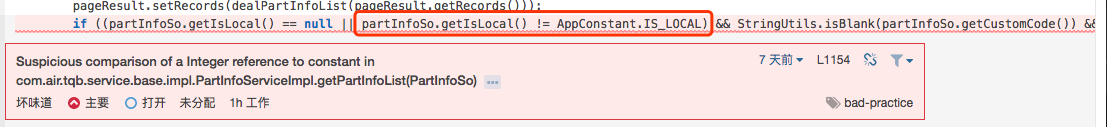
很明显sonar已经报错了,但是线上应用目前是正常的
问题
事实上经常会有面试的小伙伴或者笔试的小伙伴问这个问题
Integer的一些小知识
Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(1); Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf(1); Assert.assertTrue(i2 == i3);
按照大家的理解 valueOf会返回一个Integer 当用Integer和Integer进行比较 这是一个典型的对象比较
通常大家都会使用equals进行 但是此处用==居然可以返回true
@Test public void testValueOfIntegerIntegerGe128() { Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(128); Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf(128); Assert.assertFalse(i2 == i3); }
但是当值为128的时候居然又神奇的失败了~
Integer出现了根据数据不同 同样使用==来做判断却返回了了不同的结果!
分析
我们是否考虑过莫非Integer的小数字对象可以用==进行比较?
根据常识==只能判断是否为同一个对象
在上述代码中该同学对应的代码中
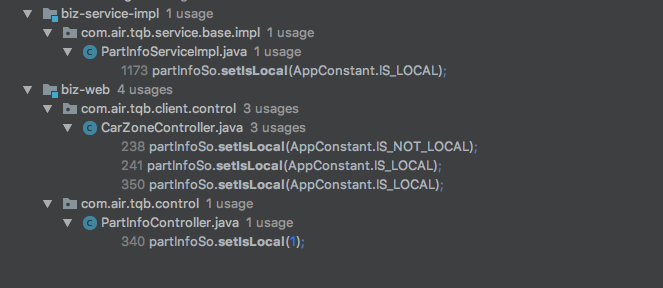
显示的使用setIsLocal进行设置只有这五处。但是有可能该对象是通过Spring的序列化来完成的。因此仍需进行考察!
源码
查看valueOf方法
/** * Returns an {@code Integer} instance representing the specified * {@code int} value. If a new {@code Integer} instance is not * required, this method should generally be used in preference to * the constructor {@link #Integer(int)}, as this method is likely * to yield significantly better space and time performance by * caching frequently requested values. * * This method will always cache values in the range -128 to 127, * inclusive, and may cache other values outside of this range. * * @param i an {@code int} value. * @return an {@code Integer} instance representing {@code i}. * @since 1.5 */ public static Integer valueOf(int i) { assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); }
很明显存在一个叫做IntegerCache的缓存了相对应的Integer的实例
当调用valueof的时候会优先判断对应是否存在指定区间内 如果确实在对应区间则直接返回对应缓存对象。
这样自然可以使用==来做判断!
private static class IntegerCache { static final int low = -128; static final int high; static final Integer cache[]; static { // high value may be configured by property int h = 127; String integerCacheHighPropValue = sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"); if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) { int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue); i = Math.max(i, 127); // Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low)); } high = h; cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1]; int j = low; for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++) cache[k] = new Integer(j++); } private IntegerCache() {} }
ntegerCache会读取vm的参数如果没有设置java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high则以127为界!
否则以对应的值作为上界。

重新执行该测试的话
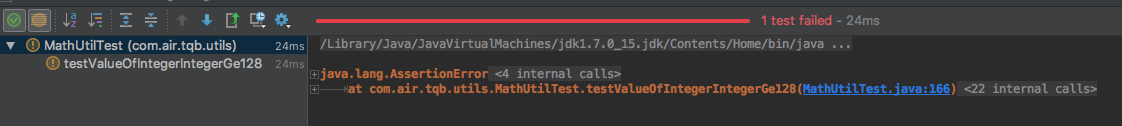
思考
Integer为啥提供该设置呢?
相对来说我们使用数字的时候基本以小数字为主
比如单价 比如个数
如果我们数量等等都要一个新的对象的话那么可能新生代需要回收的就会比较频繁!
那么很明显使用==仍然只是判断对象是否同一个对象而已!
@Test public void testIntInteger() { Integer i2 = 1; Integer i3 = new Integer(1); Assert.assertFalse(i2 == i3); } @Test public void testIntegerInteger() { Integer i2 = new Integer(1); Integer i3 = new Integer(1); Assert.assertFalse(i2 == i3); }
很明显Integer的判断相等仍然需要使用equals进行!!!





